IB Biology Virus questions
Start by reading Fullick p586- 590
and look at this excellent website:
http://www.uct.ac.za/depts/mmi/stannard/linda.html
Summary = "All the viruses (with the exception of a few bacteriophages) fall into two morphological groups:-
- those with CUBIC symmetry
- and the others with HELICAL symmetry.
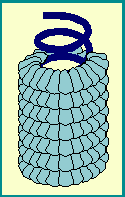
The length of the helical viral nucleocapsid is determined by the length of the nucleic acid.
The best studied example being tobacco mosaic virus.

The myxo-viruses consist of an inner nucleo-protein component with helical symmetry surrounded by an envelope of characteristic morphology.
1.
Adenovirus

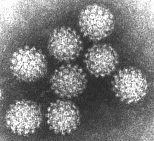
The terminology for virus components:
- The CAPSID is the protein shell that surrounds the nucleic acid.
- CAPSOMERS are clusters of protein structure units which make the capsid.
- The NUCLEIC ACID is either the DNA or the RNA inside the capsid
- The capsid may be wrapped in an ENVELOPE which is often made from "stolen" host cell membranes or viral proteins.
- The VIRION is the complete infective virus particle
QUESTIONS
Have a look at the influenza virus and tobacco mozaic virus.
- Name two diseases that are caused by virses?
- What is a Virus Capsid made from?
- Which types of chemical are viruses made from?
- What similarities are there between a bacterium and a virus?
- Which of the seven characteristics of living things are viruses unable to do? (hint: MRS GREN).
- What are the differences in the chemicals which make a virus capsid, a bacterial cell wall and
a plant cell wall
(you'll need to look this up in the text book)? - Why don't antibiotics kill plants and fungi?
- Why don't antibiotics kill viruses?